Comparison of GI Side Effects of Antidepressants
The Carlat Psychiatry Report, Volume 19, Number 8, August 2021
https://www.thecarlatreport.com/newsletter-issue/tcprv19n8/
Issue Links: Learning Objectives | Editorial Information | PDF of Issue
Topics: Antidepressants | Depression | Depressive Disorder | Free Articles | Mirtazapine | Side Effects | SNRIs | SSRIs
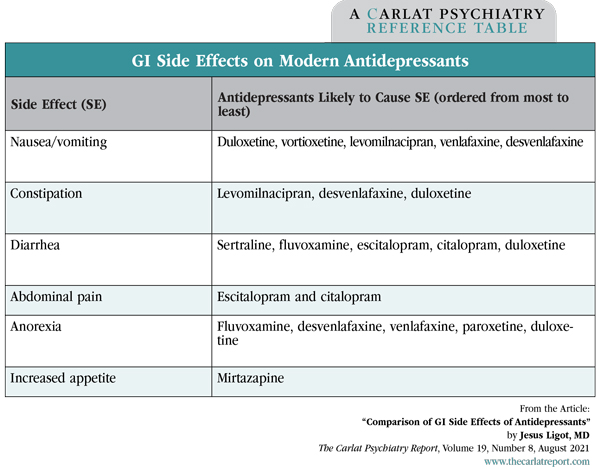
Jesus Ligot, MD. Dr. Ligot has disclosed no relevant financial or other interests in any commercial companies pertaining to this educational activity. REVIEW OF: Oliva V et al, Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2021;109:110266 TYPE OF STUDY: Meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials Antidepressants often cause gastrointestinal (GI) side effects, but it’s not clear which ones are the worst actors. A recent meta-analysis helps to clarify the picture. The investigators searched the literature and located 304 randomized, placebo-controlled trials with information on GI side effects on 15 antidepressants (including SSRIs, SNRIs, bupropion, and mirtazapine). Nausea and vomiting was the most common side effect, with the worst five antidepressants being duloxetine (odds ratio [OR] 4.33), vortioxetine (OR 4.28), levomilnacipran (OR 3.81), venlafaxine (OR 3.52), and desvenlafaxine (OR 3.51). Only mirtazapine was not associated with nausea and vomiting, which is consistent with its mechanism of action. The risk of nausea and vomiting was dose dependent for citalopram and escitalopram and became more pronounced at dosages above 40 mg/day for citalopram and 10 mg/day for escitalopram. Constipation occurred on 10 antidepressants, with levomilnacipran (OR 3.41), desvenlafaxine (OR 3.41), and duloxetine (OR 2.58) being the top three. Vortioxetine had a dose-dependent risk of constipation at dosages above 20 mg/day (which is also the maximum recommended dose). Only five antidepressants were associated with diarrhea: sertraline (OR 2.33), fluvoxamine (OR 2.29), escitalopram (OR 1.91), citalopram (OR 1.64), and duloxetine (OR 1.60). Other GI side effects were also examined and are summarized in the table. TCPR’s Take Table: GI Side Effects on Modern Antidepressants 
While most antidepressants can cause GI side effects, it appears that SNRIs and vortioxetine are the most likely to cause both nausea and constipation. True to its reputation, sertraline caused the most diarrhea. Paroxetine was associated with anorexia, suggesting this medication may have opposite effects in different patients, as other studies have associated it with weight gain. Surprisingly, the two antidepressants associated with weight loss—bupropion and fluoxetine—did not decrease patients’ appetite in this analysis.![]() To learn more, listen to our 8/9/21 podcast, “Treating Nausea on Psych Meds.” Search for “Carlat” on your podcast store.
To learn more, listen to our 8/9/21 podcast, “Treating Nausea on Psych Meds.” Search for “Carlat” on your podcast store.